Question 1: Two angles of a triangle measure . Find the measure of the third angle.
Answer:
Sum of all the angles of a triangle
Let the third angle
Therefore
Or
Question 2: Three angles of a triangle are in the ratio of . Find the angles of the triangle.
Answer:
Let the angles be
Therefore
Or
Therefore the angles are
Question 3: One angle of the triangle is and the other two angles are equal. Find the measure of each angle of the triangle.
Answer:
Let the two equal angles be
Therefore
Or
Therefore the angles are
Question 4: One angle of the triangle is and the other two angles are in the ratio
. Find the measures of each of the unknown angles.
Answer:
Let the two unknown angles be
Therefore
Or
Or
Therefore the two angles are
Question 5: Three angles of a triangle measures . Find the value of
and the measures of all the angles.
Answer:
Or
Hence the angles are
Question 6: In . Find the value of
and the measure of all the angles of the triangle.
Answer:
or
Hence
Question 7: In . Find the value of x and the measure of all the angles of the triangle and show that the triangle is an isosceles triangle.
Answer:
Hence
Question 8: In . Find the angles of the triangle.
Answer:
Let
Question 9: In the adjoining figure, it is given that . Find the value of $latex
.
Answer:
Note: Sum of angles of adjacent angles on a straight line
Note:Sum of all angles of a triangle
Question 10: In the adjoining figure, it is given that and
are bisectors of
respectively. Find the measure of
Answer: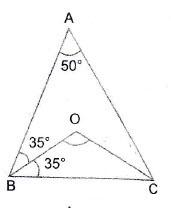
Let
Since
Question 11: Using the information given in the adjoining figure, find the value of 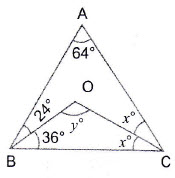
Answer:
Question 12: In the adjoining figure, is a straight line,
. Find
Answer: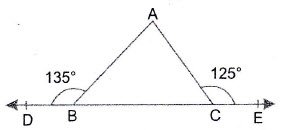
Therefore
Question 13: Find, giving reasons, the unknown angles marked by in the following figures.
Answer:
i)
ii)
iii)
iv)
v)
vi)
Given which means
Question 14: In the adjoining figure, if , find the value of
and hence, find the measure of
Answer: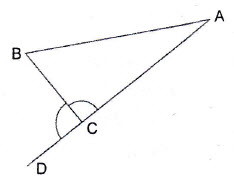
Question 15: In , side AC has been produced to D. If
, find the measure of
Answer:
Let
Therefore
Question 16: In the adjoining figure, it is given that: . Find the measure of
Answer: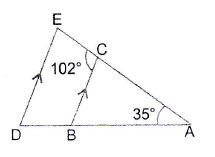
i)
Note:Co-interior Angles
ii)
iii)
Question 17: In the adjoining figure, it is given that:. Find
Answer: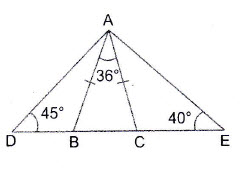
Therefore
i) & ii) Hence
iv)
iii)
Question 18: Using the information given in the adjoining figure, calculate the values of 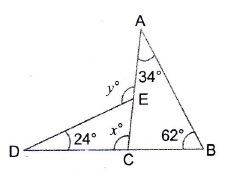
Answer:
In
In
Question 19: Sides have been produced to D and E respectively.
are bisectors of
respectively. If
, find the measure of

Answer:
Given
Question 20: In the adjoining figure, it is being given that . Find the value of
.
Answer: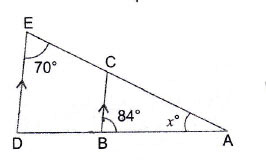
Note:Alternate angles
Question 21: In the adjoining figure, it is being given that
. Find the value of
.
Answer:
In
In
Question 22: In the adjoining figure, it is given that
Find the value of
Answer:
In 
In
In
Question 23: In the adjoining figure,
Answer: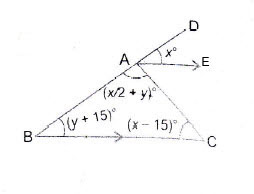
In
Since
Note:Alternate Angles
Substituting ii) in i) we get
Substituting the value of
Question 24: In the adjoining figure, . Find the values of
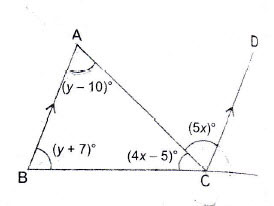
Answer:
In
Since
Substituting ii) in i) we get
Substituting in ii) we get
